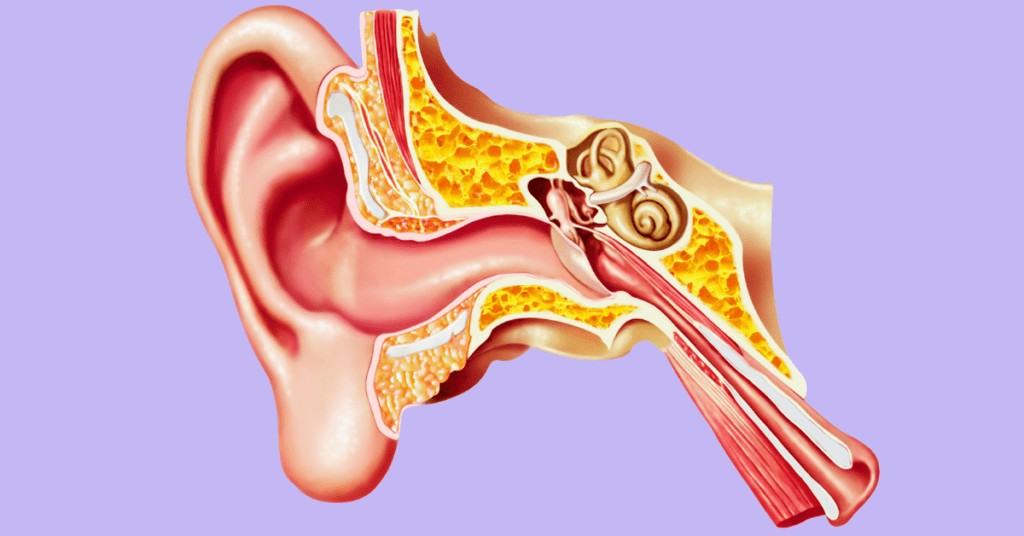
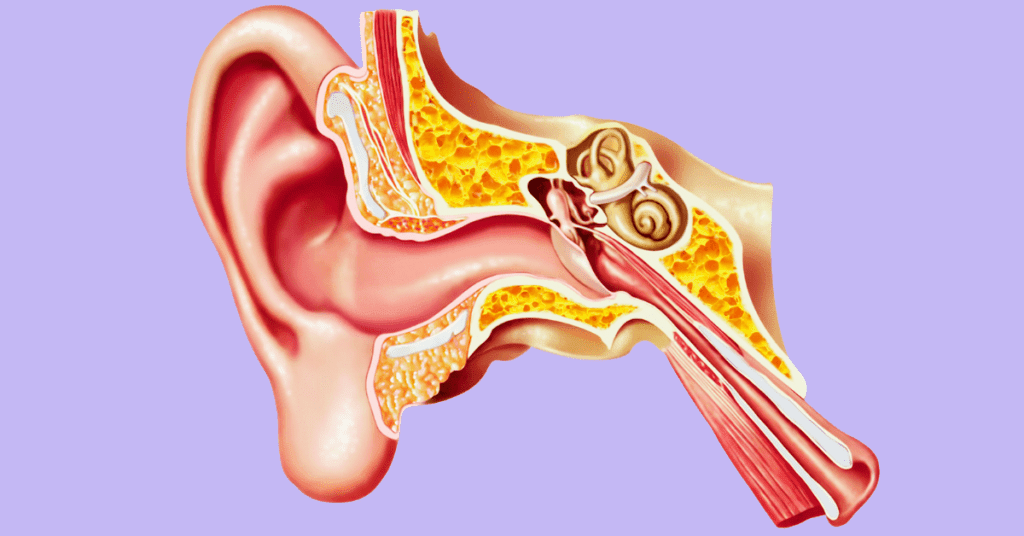
The eustachian tubes are a small passageway that connects your middle ear to the back of your throat, also known as the nasopharynx. There is one eustachian tube in each of our middle ears, which is the area located behind the eardrum. The tube is about 36 millimeters long and part of it is made of bone, while the part closest to your nose and upper throat is made of cartilage.
What Do The Eustachian Tubes Do?
Eustachian tubes help equalize air pressure inside of your ears and ventilate the middle ear cavity, which is an air-filled space. They also help drain fluid or secretions that can build up behind the eardrum. Most of the time, the eustachian tubes remain closed, but they open or close when swallowing food, chewing gum, or yawning.
What Is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
When the eustachian tubes aren’t working properly, eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) or chronic eustachian tube dysfunction can happen in one or both ears. For example, the valves may remain open or closed the majority of the time, causing issues like middle ear pressure and ear pain in one or both ears.
"Treble Health helped me reduce my tinnitus by about 80%, and now I can live my life again!"



"Treble Health helped me reduce my tinnitus by about 80%, and now I can live my life again!"
– Steve D.
Book a free consultation to learn which Treble Health solution is right for you. Join Steve and thousands more who have found lasting tinnitus relief.
There are three common types of eustachian tube problems: patulous ETD, obstructive ETD, and baro-challenge-induced ETD. Patulous eustachian tube dysfunction is when the tubes stay open. Obstructive eustachian tube dysfunction is when the tubes don’t open properly, allowing fluid to build up in the middle ear space. Baro-challenge-induced eustachian tube dysfunction is similar to obstructive ETD, but it is caused by atmospheric pressure changes.
What Causes Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
There are several causes of ETD. Some of the common causes include: chronic nasal allergies, weight loss, stress, anxiety, sinusitis, neoplasms (abnormal tissue growth), common cold, pollution, cigarette smoke, and altitude changes. Chronic neuromuscular or immunological disease, acid reflux, or a cleft palate can also be an underlying cause for ETD.
What Are the Signs And Symptoms Of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
Symptoms will vary from individual to individual and may change throughout the course of ETD. If the eustachian tubes stay open, for instance, internal sounds like breathing or swallowing are altered and sound louder. If the eustachian tubes remain closed, individuals will feel ear fullness and pressure. Fluid in the middle ear may develop in a condition known as otitis media. Fluid in the ears can also cause muffled hearing. These hearing difficulties and subsequent hearing loss is usually temporary. However, if the fluid becomes infected, it can lead to ear infections, which can cause severe pain in one or both ears.
If ear infections are left untreated or the infected fluid does not drain on its own, it can start to spread to other parts of the ear and head, including the inner ear. In some instances, the fluid can cause a tympanic membrane perforation. This will often result in severe pain and fluid or mucus may be felt inside of the ear canals.
Some individuals with ETD will experience other ear problems, like frequent ear popping or clicking, balance issues, and even tinnitus, as a result of the inability of the eustachian tubes to equalize pressure in the middle ear. The affected ear may experience other symptoms that the non-affected ear does not experience.
How Can Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Cause Tinnitus?
If the eustachian tube isn’t opening, it can cause pressure to build behind the eardrum. While pressure is building, it can cause tinnitus. Tinnitus sounds like thumping, humming, or roaring and may be a result of increased pressure on the vascular structures in the middle ear. If the eustachian tubes remain open, it alters the way sound travels through the head and ears. Sound may travel from the nasal cavity up to the ears, causing people to hear their own voice, breathing, chewing, swallowing, or even the rushing of blood flow.
Who Does Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Affect?
Both adults and children are susceptible to eustachian tube dysfunction; however, children are more likely to have eustachian tube problems. Anatomically, a child’s eustachian tubes are more horizontal than those of adults. The tubes in an adult are angled downwards, which allows fluid to drain more easily. Since the tubes in children are more horizontal, fluid is more likely to build up in the middle ear. Adult eustachian tube dysfunction is less likely to occur, but nonetheless is possible. For example, adults are more likely to experience baro-challenge-induced ETD than children.
How Is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Diagnosed?
A medical doctor, like an otolaryngologist or ear nose and throat (ENT) specialist, will look inside of your ear to see how your eardrums are moving in response to air pressure changes. They may have you perform the valsalva maneuver, which will require you to pinch your nose, close your mouth, and try to push air out of your mouth. A doctor may also check your nasal passages for any signs of inflammation or irritation. If they suspect blocked eustachian tubes, they may refer you to an audiologist for further testing.
To assess ETD, an audiologist will perform a hearing test to determine if there are any signs of conductive hearing loss, which would signal an issue in either the outer or the middle ear. They will also perform tympanometry testing, which assesses the mobility of the eardrum. Abnormal responses can indicate issues like blocked ear canals due to cerumen, negative or positive pressure behind the eardrum, or even the presence of fluid in the middle ear space.
How Long Does Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Last?
ETD is usually temporary and will resolve on its own within one to two weeks. If you experience recurrent episodes of eustachian tube problems or it lasts longer than two weeks, you should visit a medical professional.
What Are The Treatment Options For Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
In most cases, eustachian tube problems resolve on their own. A medical doctor will determine the appropriate treatment option for the situation at hand. If the eustachian tube dysfunction is believed to be the result of allergies or nasal congestion, then a medical doctor may prescribe a steroid nasal spray or other form of decongestant or antihistamine. Surgical treatments are also available for those with eustachian tube dysfunction. If middle ear fluid has developed, then a physician may make a tiny incision in the eardrum to suction out fluid and allow any remaining fluid to drain. This small incision will usually heal up on its own.
For adults, ETD procedures to prompt drainage are usually completed in-office, but for children, this is usually completed under anesthesia while a pressure equalization tube is placed into the eardrum. These are often referred to as ear tubes. In rare cases, a small balloon can be inserted into the eustachian tube to keep the eustachian tube open and alleviate middle ear pressure. The symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction usually resolve or improve following treatment and related conditions also typically respond to intervention, including tinnitus treatment.
How Long Does It Take To Recover from Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Treatment?
Depending on the treatment, individuals will likely feel an improvement in their symptoms either immediately or within a few days. For this reason, it is important to follow up with a medical doctor if you are experiencing symptoms related to eustachian tube dysfunction. This is a condition that can often be treated, so that you don’t have to live with any unpleasant symptoms, like ear pain, fullness, or hearing loss.
Next Step: Book Free Consultation
- 75% of patients reduced their tinnitus within three months after following our recommendations.
- "I feel like Treble Health literally gave me my life back." - Randy S. (verified customer)
- Join thousands of people who have reduced their tinnitus after scheduling a free consultation.