Post nasal drip is frequently linked to allergies and colds. Unlike a standard runny nose, this particular type of mucus secretion can cause a host of issues as diverse as a sore throat and damage to the inner ear. Is it possible for some times of nasal congestion to lead to auditory issues like tinnitus? First, let’s take a look at what post nasal drip actually is, and how a condition that causes facial pain and general discomfort in the nasal cavity can impact the ear canal and potentially lead to tinnitus.
What Is Post-Nasal Drip?
Glands in the nose and throat constantly make mucus to moisten and clean nasal lining, moisten breathed air, trap and clear what is inhaled, and help fight infections. We don’t typically notice the mucus because it mixes with saliva, naturally drips down the back of the throat, and is swallowed. Post-nasal drip is a condition in which the sinus cavities fill with mucus, but instead of running from the nostrils, as is frequently seen when you have a cold or sinus infection, mucus drips down the back of the throat in excess. Post nasal congestion can be problematic for several reasons, the most pertinent of which is the ability of this mucus to essentially clog the drainage of the eustachian tube and ultimately damage the ears.
Post-Nasal Drip And Tinnitus
When the nasal cavity fills with mucus and blocks the eustachian tubes, changes to air pressure and normal function occur. Tinnitus can result when ears are no longer able to drain and reach equilibrium as a result of post nasal drip.
"Treble Health helped me reduce my tinnitus by about 80%, and now I can live my life again!"

"Treble Health helped me reduce my tinnitus by about 80%, and now I can live my life again!"
– Steve D.
Book a free consultation to learn which Treble Health solution is right for you. Join Steve and thousands more who have found lasting tinnitus relief.
Symptoms of post-nasal drip can include coughing, frequent swallowing, hoarseness, bad breath (halitosis), nausea or vomiting from excess mucus draining into the stomach, and ear or throat discomfort, as well as ear infections. Post-nasal drip is often an underlying cause of various issues, including eustachian tube dysfunction. Addressing the root condition can frequently alleviate symptoms. Nasal congestion, sinus infections, and ear infections can result from post-nasal drip or cause it, which can directly relate to the development of tinnitus.
The Eustachian Tube And Tinnitus
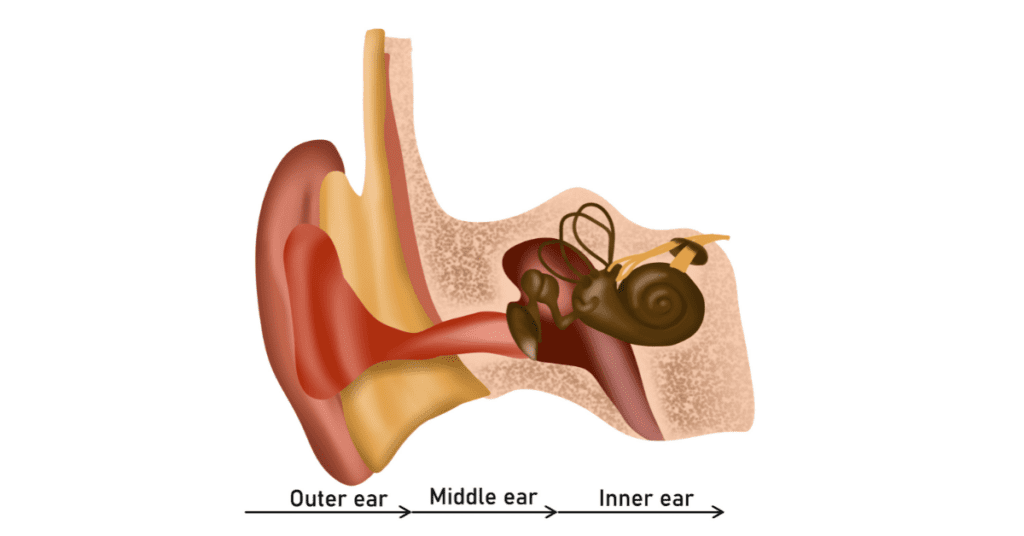
The eustachian tube is a small passageway that connects the throat to the middle ear where the eardrum is located and helps maintain normal pressure in the middle ear space. Eustachian tube problems can occur if post-nasal drip flows down the back of the throat to the end point of the tubes and clogs them.
Nasal drip is not the only condition affecting eustachian tubes that can lead to tinnitus, however. Infections and poor drainage without drip are also possible instigators for tinnitus, as all parts of the sinuses are interconnected systems that rely on the health of one another to remain stable. When patients experience dysfunction in one area of the sinus cavities, as might occur in sinusitis and other sinus infections, tinnitus may not be far behind. Tinnitus relief is often not far behind the clearing of the original cause, whether it is a sinus infection, an infection of the middle ear, or something else entirely.
Ear Congestion And Tinnitus Symptoms
While it may not initially seem as though congestion in the ear is related to the development of hearing issues, sinus congestion and corresponding ear congestion can lead to tinnitus symptoms, whether those symptoms lead to persistent tinnitus or temporary symptoms. Ear congestion can be a result of excess mucus, but can also be a symptom of blowing the nose too frequently or with too much force. Congested or plugged ears often muffle sound, and can cause headaches and a persistent feeling of pressure in the sinuses. When ear congestion resolves, whether that comes after you treat sinusitis or simply chew some gum, ringing in the ears may resolve.
Ear Infections, Sinus Infections, and Tinnitus
Ear infections in the ear canal (outer ear) or, in this case, a middle ear infection can cause a decrease in hearing or temporary hearing loss, which can result in tinnitus. Chronic post-nasal drip can result in temporary loss of hearing (typically conductive hearing loss), which can result in tinnitus. Inner ear related hearing loss (called sensorineural hearing loss) can also cause tinnitus, but there is not currently evidence that post-nasal drip has direct effects on the inner ear. An audiological exam can help determine the type and extent of hearing loss.
Chronic sinus infections are a known cause of post-nasal drip and tinnitus, largely because nasal congestion related to a sinus infection causes abnormal pressure in the middle ear and impair hearing function. Ear pressure causes damage and phantom sound in the same way as an ear infection, and can impact hearing levels as well as create a sensation of phantom sounds that include ringing, rushing, or roaring.
Treating Post-Nasal Drip

Treatments for post-nasal drip run the gamut, from at-home remedies that can be completed easily, to medications. The most common recommendations for post-nasal drip treatment include the following:
- Exposure to steam, taking a warm shower, or drinking warm beverages like broth or tea. These are all common home remedies, but are intended to relieve symptoms rather than directly address a bacterial infection or more serious issue affecting the nasal passages.
- Using a humidifier. Again, this can help with post-nasal drip that is not directly related to an actual infection, but is due more to allergies or other non-infectious causes.
- Hydrating adequately. Dryness can be a source of post-nasal drip, so making sure that you are adequately hydrated and supporting your body can help alleviate symptoms. As previously mentioned, the nasal passages require moisture, and inadequate hydration can increase the risk of experiencing an ear disorder if proper mucus excretion is not present or possible.
- Nasal irrigation. Nasal irrigation is accomplished by essentially “flushing” the sinuses, most often with a saline solution. This can help ease some pressure on the mucous membranes and support a healthier level of secretion, thereby decreasing the likelihood of experiencing ear pressure and subsequent damage to the ear drum.
- Medication or decongestants such as antihistamine, oral decongestant, or guaifenesin. Depending on the cause, doctors may prescribe or suggest medications and decongestants, though more intense cases may require nasal corticosteroids to effectively relieve sinus pressure.
- Sleeping propped up on pillows. By sleeping propped up on pillows, you can help mucus flow in a steadier, slower manner, and ease the effects of post-nasal drip.
Tinnitus treatment related to post-nasal drip starts by treating the underlying condition. Tinnitus relief typically aligns with relief of post-nasal drip or another related condition, so determining if the root is from an external source or is derived from something else altogether is essential in finding relief from tinnitus symptoms.
Other Causes Of Tinnitus
Different types of eustachian tube dysfunction can lead to hearing concerns, but there are actually numerous traumas and conditions that can cause ringing in the ears, both in an acute form and in a chronic form. The most common causes of tinnitus include:
- Loud noise exposure. Loud noise exposure can cause tinnitus, as it damages the hair-like structures within the ear, which helps appropriately deliver and filter sounds. When these structures are damaged, ears can perpetually or intermittently sound as though they are ringing.
- Ear infection and blockage. Many factors come into play here, but persistent or chronic ear infections and blockages can also damage the ear and lead to ringing in the ears.
- General hearing loss. General hearing loss can have numerous causes (and numerous treatment options), but tinnitus frequently accompanies individuals who suffer from hearing loss, whether it is due to age or another factor.
- Injuries to the head or neck. Head and neck injuries can negatively impact the nerves and processes within the head and neck, which affects the efficiency of sounds coming into auditory pathways, and how those sounds are registered.
- Medication side effects. Some medications list tinnitus as a possible side effect, while others have hearing loss as a potential side effect. In either case, people taking these medications may find themselves experiencing ringing, buzzing, or roaring in the ears.
Although not all of these conditions are reversible, there are numerous tinnitus treatment options available to help manage symptoms and increase quality of life.
Conclusion
Many patients who see an audiologist or ENT for issues related to sinuses and tinnitus find themselves with a case of related conditions. From allergies to sinusitis, to dry air and congested ears, the sinus cavities are all highly related to one another, and any dysfunction, injury, or illness in one will result in changes to the other. By addressing allergies, sinusitis, and other common causes of blocked eustachian tubes, patients may be more likely to see changes to tinnitus symptoms and experience relief.
At Treble Health, our audiologists understand the importance of addressing underlying conditions and looking at a tinnitus patient as a whole. Our audiological team has years of experience working with tinnitus patients from all backgrounds, including those whose tinnitus symptoms are related to issues involving nasal passages and conditions affecting the eustachian tubes. Take your first step toward tinnitus relief by reaching out today to schedule a complimentary telehealth consultation. In this 20-minute Zoom consultation, you can expect to receive answers to your questions, a personalized plan to address your unique set of symptoms, and a thorough recounting of your symptoms and history.
From chronic sinusitis to regular bacterial infections, our team is familiar with all types of tinnitus onset. Reach out today to start the path to relief!
Next Step: Book Free Consultation
- 75% of patients reduced their tinnitus within three months after following our recommendations.
- "I feel like Treble Health literally gave me my life back." - Randy S. (verified customer)
- Join thousands of people who have reduced their tinnitus after scheduling a free consultation.