When the term “oxidative stress” is mentioned, what comes to your mind? Regardless of your familiarity with the concept, oxidative stress impacts your life daily. Our bodies constantly face environmental factors and undergo habits that can trigger a protective response against potential harm. However, as these stressors accumulate and surpass the body’s natural antioxidant defense, oxidative stress ensues. This condition can inflict damage on fatty tissues, DNA, and protein structures, setting off a domino effect of detrimental outcomes. Among these are the numerous comorbid conditions often found in individuals with tinnitus. Delving deeper into the dynamics of oxidative stress will shed light on its relationship with ailments like tinnitus, and unravel how it impinges on various bodily systems.
Oxidative Stress: The Basics
Understanding oxidative stress–what it is, and how it works in the body–requires first understanding what free radicals and antioxidants are. If you have been present in wellness spheres in recent years, you have likely heard the terms antioxidant and free radical. These terms are frequently used in wellness circles to prescribe certain remedies or lifestyle changes–many of them with good reason. However, without fully understanding what each of these things are, it can be difficult for tinnitus patients or people as a whole to benefit from antioxidant therapy and truly understand how to lower their oxidative stress index.
"Treble Health helped me reduce my tinnitus by about 80%, and now I can live my life again!"

"Treble Health helped me reduce my tinnitus by about 80%, and now I can live my life again!"
– Steve D.
Book a free consultation to learn which Treble Health solution is right for you. Join Steve and thousands more who have found lasting tinnitus relief.
The two key figures in oxidative stress are free radicals and antioxidants. Free radicals are oxygen-containing molecules with an uneven number of electrons. Because unpaired electrons cannot “rest,” they are essentially forced to roam the body in search of another molecule with which to pair. Free radicals may cause large chain chemical reactions in the body, effectively “stealing” pairings and causing the body to experience aging, inflammation, etc. as its systems are thrown into imbalance. The reaction caused by free radicals is called oxidation, which can be beneficial to the body, but can also be extremely harmful. Common examples of reactive oxygen species include superoxide, hydroxyl radical, and nitric oxide radical.
Antioxidants are molecules with a free electron that can be “donated” to that unpaired electron without becoming unstable themselves. When that single electron is paired up, its reactivity falls away, and the molecule can become more stable and functional within the body. As you can imagine, antioxidant therapy that prevents a host of free radicals from assaulting the body can lessen oxidative stress and positively impact the body. Some common examples of antioxidants include vitamins A, C, and E.
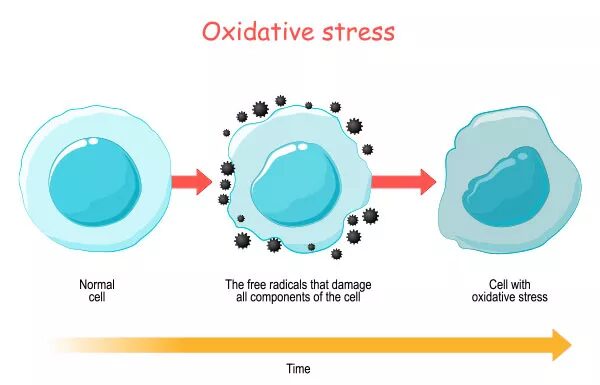
Oxidative stress, put simply, is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. This can cause damage to organs and tissues, and can be at the root of many different issues, ailments, and diseases. From simpler things, like aging more rapidly than your age might suggest, to more substantial things, like chronic disease, oxidative stress has a very real impact on the body. Fortunately, limiting or lessening oxidative stress is not an impossible task, and implementing a balanced and healthy lifestyle can help reduce cellular stress response, and improve your total antioxidant status. While different conditions and even genetic markers may increase risk factors for oxidative stress, no one is definitively doomed to show signs of oxidative stress markers long-term.
Effects Of Oxidative Stress In The Body
Long-term oxidative stress has the ability to damage DNA structures within the body, leading to oxidative stress markers and increased risk factors for conditions tied to chronic information, including the following:
- Diabetes
- Hypertension/high blood pressure
- Atherosclerosis
- Cancer
- Heart Disease
- Neurodegenerative diseases
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Alzheimer’s Disease
Again, while oxidative damage does not guarantee these conditions will develop, people can typically experience a significant reduction in their risk factors for developing these diseases. From actively engaging in antioxidant treatment like antioxidant therapy, or working through the subjective discomfort of implementing new lifestyle choices to lessen oxidative damage, there are ways to limit the effects of chronic oxidative stress and lessen oxidative stress biomarkers overall.
What Is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is a hearing condition in which a person experiences the sound of ringing, buzzing, hissing, clicking, without an identifiable external source. There are different types of tinnitus, including idiopathic tinnitus, and tinnitus caused by noise induced hearing loss, but all of them carry the common characteristic of phantom noises without an external source. Tinnitus patients can hear sounds in one or both ears, and the symptoms can be experienced as mild or severe, and acute or chronic.
While many people remain unfamiliar with tinnitus, tinnitus patients make up between 10-25% of the population, and 20% of those tinnitus sufferers consider their symptoms to negatively impact their daily life. While there are many different potential causes for tinnitus, it has been suggested that oxidative stress can play a role. Other common causes including the following:
- Hearing Loss
- Sensorineural hearing loss. The cause and specific type of sensorineural hearing loss can vary, including noise induced hearing loss, age-related hearing loss (called presbycusis), inner ear disorders (i.e. Meniere’s Disease), and sudden hearing loss. All of these can be related to oxidative stress, but are not necessarily linked, and may not improve when antioxidant therapy is administered. This is true of noise induced hearing loss and other types of hearing loss not directly tied to oxidative stress, though any improvements to health can help hearing health overall.
- Conductive hearing loss. Conductive hearing loss is so named because it occurs when there is an obstruction of sound through the outer ear and/or middle ear, causing a reduction in the transmission of sound. There are many different possible root causes of this type of loss, but some common conditions include otitis externa (swimmer’s ear), otitis media, otosclerosis, cholesteatoma, and cerumen blockages. Tinnitus intensity for these causes often will depend on whether or not hair cells were damaged and how advanced the condition in question is.
- Mixed hearing loss. Mixed hearing loss describes a combination of sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss. Examples of combined sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss could include the onset of age related hearing loss, combined with excess ear wax, or the presence of both noise induced hearing loss and an ear infection.
- Head Injury/ Neck Injury
- Medications/Ototoxic Exposures
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Kidney Disease
- Autoimmune Disorders

Although this list is certainly not exhaustive, there are many possible causes of tinnitus, including mental health concerns and increased stress. Often, when potential tinnitus patients complete a tinnitus handicap inventory, some of the more likely underlying causes can be seen, and practitioners can get a clearer picture of different interventions that may be of the greatest help to relieve symptoms.
Research Supporting The Relationship Between Oxidative Stress And Tinnitus
Understanding the body’s oxidative stress index and its effect on hearing health is important to understand cellular stress response, tinnitus intensity, and changes or damages to the inner ear. Evaluating these relationships can help determine the root of not only tinnitus, but also age related hearing loss and other links to oxidative stress. One study determined the presence of oxidative stress in relation to tinnitus, and found a considerable tie.
A Comprehensive Study Of Oxidative Stress In Tinnitus Patients
In the aforementioned study, the goal of the study was to investigate the role of oxidative stress in tinnitus patients, as well as to investigate lipid peroxidation, total antioxidant status (TAS), total oxidant status (TOS), and oxidative stress index (OSI) parameters. The findings were then compared with a healthy control group without symptoms of tinnitus. The study group contained 70 patients total: 35 patients had bilateral tinnitus and sought help from an ear, nose, and throat clinic, while 35 were used as the control group, without idiopathic tinnitus or another series of tinnitus symptoms.
The study eventually found that the total thiol, native thiol levels, and LOOH, total antioxidant status and total oxidant status differed from those of healthy patients, suggesting oxidative stress is at least partially responsible for symptom onset. TOS and OSI levels were increased, and total antioxidant status levels were substantially lower than the control group levels. The findings suggest that oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes were significantly different from patients in the healthy control group. Tinnitus patients are affected by and exposed to potent oxidative stress.
Additional Notable Findings
One study found that free radicals in the cochlea were linked to sensory epithelial damage, which can lead to damages to the inner ear and subsequent hearing loss. This study suggests that antioxidant therapy using Renexin is a useful intervention for some issues regarding hearing health and oxidative stress. Another study determined that oxidative stress actually plays a crucial role in the etiopathogenesis (or cause and development of a condition) of tinnitus.
Issues within the inner ear can lead to chronic tinnitus, and oxidative stress may be one of these, as oxidative stress plays a role in endothelial dysfunction. Yet another study determined that loud noise actually induced free radicals’ release of superoxide radicals, hydroxyl radicals, and hydrogen peroxide, all of which may cause damage to the cochlear hair cells partially responsible for healthy hearing.
Ultimately, a consistent number of studies found that there is a correlation between oxidative stress and tinnitus, whether through impaired serum total antioxidant capacity or an overload of stress-causing free radicals. Free radicals in the body can lead to damage to cochlear structures, which can result in the onset of endothelial dysfunction and related tinnitus symptoms and prompt a chronic tinnitus diagnosis or a spike in existing symptoms.
How To Reduce Oxidative Stress
The roots of oxidative stress are many and varied. There are typically several different arenas leading to the onset of oxidative stress. These include lifestyle habits and practices, dietary habits, environmental factors (pollution, cigarette smoke, ozone, pesticides, and radiation), and immune responses leading to inflammation. Fortunately, many of these issues are able to be addressed at home, in order to support health and reduce the level of oxidative stress in the body.
Lifestyle And Dietary Changes
Eating a balanced, healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables is one of the best ways to lower oxidative stress via eating habits. Limiting your intake of processed foods (especially those high in sugars and fats) can also help reduce free radical damage. From there, exercising regularly and reducing stress can help limit the effects of free radicals and increase the activity of antioxidants in the body.
Environmental Exposure Changes And Reductions

Avoiding and reducing exposure to pollution and harsh chemicals is not always possible, but doing so can help limit the body’s antioxidant enzyme imbalance. From limiting them in the home by avoiding them in cleaning products and other potentially harmful sources, to avoiding these same things in personal products and at work, limiting environmental exposures can significantly help reduce oxidative stress. Quitting smoking is another excellent way to reduce oxidative stress.
Addressing Immune Responses
It has been touched on before, that immune responses can contribute to tinnitus. This is also true of the immune system and oxidative stress. If an overactive or inappropriately reacting immune system is present, consult with a doctor to help limit the resulting oxidative stress.
Tinnitus Treatment Options
Whether or not your tinnitus symptoms are caused or exacerbated by oxidative stress, it is important to find the treatment solution that works best for you. The most common tinnitus treatment options include the following:
- Hearing aids. Hearing aids help restore missing auditory input to the brain, and deliver the environmental awareness necessary to help distract the brain from the sounds of tinnitus and seemingly limit tinnitus loudness. They can also be used to deliver sound therapy, if they are equipped to do so.
- Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT). Combining hearing aid amplification and educational counseling, TRT provides these interventions using a structured approach in order to address both the acoustic and emotional aspects of tinnitus to offer relief from symptoms.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). CBT is a type of specialized counseling, which can help shift negative thoughts about tinnitus. Tinnitus patients can experience more neutrality toward their symptoms, and find a greater sense of control and acceptance.
- Sound therapy. Sound therapy is an intervention that aims to reduce the awareness of tinnitus sounds in order to provide relief through the use of targeted sounds.
Reducing systemic oxidative stress can help limit the effects of oxidative dress on hearing health, whether that is accomplished through specific antioxidant treatment or making lifestyle and dietary changes to reduce oxidative stress and increase antioxidant compounds. While the subjective discomfort of tinnitus can mean being unable to restore normal hearing, there are numerous interventions that can reduce oxidative stress parameters and improve symptoms of tinnitus.
Treble Health Can Help
We know that tinnitus is not merely a persistent, intrusive noise but a condition that can profoundly impact your emotional and overall well-being. If you’re looking for help along your tinnitus journey, we encourage you to schedule a complimentary telehealth consultation with our audiology team. During this complimentary, 20-minute Zoom consultation, our team can answer any questions that you may have, and provide personalized, actionable solutions to navigate through the comprehensive world of tinnitus management. This is more than a call – it’s a step towards reclaiming tranquility and assurance in your auditory world, free from obligations and entirely tailored to your unique experiences and needs. Click here to schedule your complimentary consultation.
Next Step: Book Free Consultation
- 75% of patients reduced their tinnitus within three months after following our recommendations.
- "I feel like Treble Health literally gave me my life back." - Randy S. (verified customer)
- Join thousands of people who have reduced their tinnitus after scheduling a free consultation.