Have you ever heard a thumping, tapping or clicking noise in your ears that occurs randomly and seemingly for no reason?? Although uncommon, you may be experiencing a condition known as Tensor Tympani Syndrome – TTS (also called Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome – TTTS). While Tensor Tympani Syndrome is not considered dangerous, it may cause significant distress and frustration for anyone struggling to understand and manage the symptoms caused by the muscle spasm of the middle ear muscle (the Tensor Tympani).
What Is The Tensor Tympani Muscle?
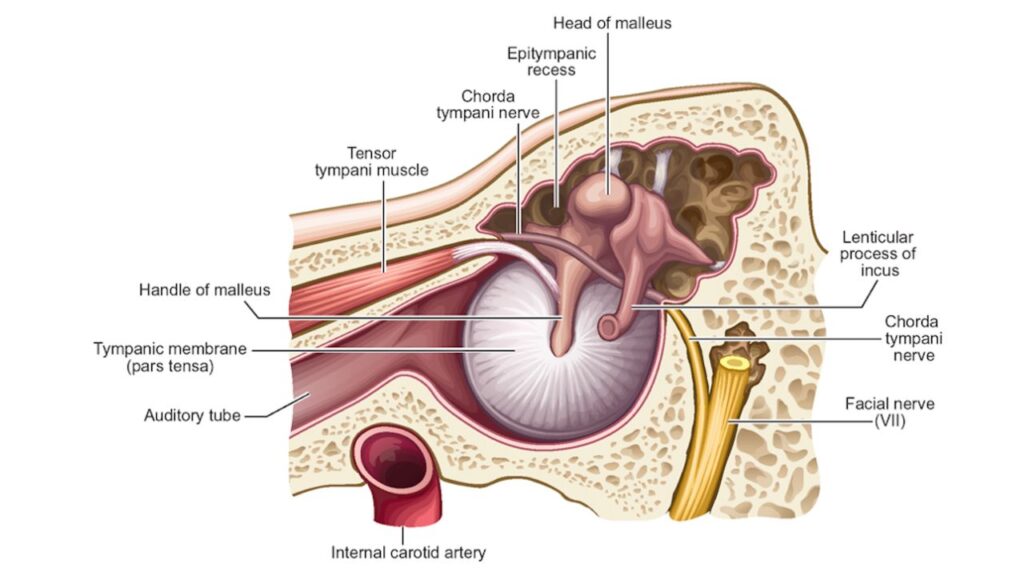
Located in the middle ear (called the middle ear cavity), the tensor tympani muscle is one of two middle ear muscles that support the three middle ear bones, called the ossicles. The Tensor Tympani is attached to the malleus, the largest of the ossicles. The malleus, in turn, is connected to the tympanic membrane on one end and the other two ossicles, the incus and stapes on the other, which then connect to the inner ear.
"Treble Health helped me reduce my tinnitus by about 80%, and now I can live my life again!"


"Treble Health helped me reduce my tinnitus by about 80%, and now I can live my life again!"
– Steve D.
Book a free consultation to learn which Treble Health solution is right for you. Join Steve and thousands more who have found lasting tinnitus relief.
The function of the middle ear is to deliver the sound waves from the outer ear to the cochlea (the sensory organ of hearing) of the inner ear. When sounds hit the eardrum, the ossicles vibrate; the louder the sound, the greater is the vibration. When sounds become loud (over 70dB), the tensor tympani muscle contracts, along with another muscle, the stapedius, to help stabilize the ossicles and reduce their vibration, thus reducing perceived volume. The actions of the middle ear muscles are called middle ear muscle reflexes or acoustic reflexes, and audiologists are able to measure acoustic reflex function using a test called the middle ear impedance.
The action of the tensor tympani is to pull the tympanic membrane inward, increasing tympanic membrane tension. You can think of the tensor tympani muscles as a kind of internal calming mechanism that ensures that you’re able to stabilize volume and react to fluctuations in noise–as well as offering the delicate inner ear some protection from loud sounds. It also plays a role in the ventilation of the middle ear by way of the Eustachian Tube. In some patients, when this middle ear function is impaired, hyperacusis (a perception of sounds being much louder than they actually are) can develop. There is also a suggested theory, that in those with severe hyperacusis even just the thought of a loud sound can trigger the tensor tympani muscle to contract leading to symptoms of Tensor tympani syndrome (TTS).
What Is Tensor Tympani Syndrome?
The middle ear muscles can also contract involuntarily (without the loud sound being present), producing an audible or fluttering sensation called the middle ear myoclonus (MEM). Middle ear myoclonus can be the result of contraction or a muscle spasm of either the tensor tympani or the stapedius muscle. Middle ear myoclonus is typically related to Eustachian tube dysfunction in which the dysregulation of the middle ear pressure triggers a spasm of the tensor tympani resulting in ear drum fluttering.
The middle ear muscles not only help protect our ears from loud sounds, their activation can also be triggered by physiological actions, like talking, chewing, swallowing, or even being startled.
Sometimes, the tensor tympani muscle can experience a spasm and contract even without loud sounds provoking a reflex. This is known as our Acoustic Reflex, and is present in a healthy auditory system. However, this hyper-reaction may also be caused by anxiety resulting from tinnitus or hyperacusis. This is because people who suffer from either condition are more likely to be in a persistent, low-level state of anxiety, fearing the sudden onset of noises or ear pain. The tensor tympani muscle contraction can also be caused by general anxiety.
Symptoms Of Tensor Tympani Syndrome



Contraction of the tensor tympani muscles may result in a variety of sensations. The following are the tensor tympani myoclonus syndrome symptoms consistent with this condition:
- Clicking, thumping or buzzing tinnitus
- Sensation of fluttering in the ears (AKA: tympanic flutter)
- Sharp pain in and around the ear
- Dull ache in the ears
- Sensation of pressure or blockage in the ears
- Pain, numbness or burning sensations around the ear
- Mild vertigo
- Nausea
- Headaches
- “Muffled” or distorted hearing
Causes Of Tensor Tympani Syndrome
Currently, there is not a lot of research about TTS, but we do know that all of these sensations are generally more prevalent in patients with tinnitus and hyperacusis. Hyperacusis (an increased sensitivity to normal levels of loudness) can develop when a person has a conscious or subconscious fear of loud sounds as potentially dangerous to the hearing mechanism. It’s unclear if TTS symptoms happen to simply overlap with everyday sounds causing pain, or if there may be some relationship between the two conditions and another condition altogether, like anxiety.
In studies, hyperacusis severity appeared to increase symptom prevalence of TTS. The more severe the hyperacusis, the greater and more constant TTS symptoms appear to be. Unfortunately, this can create a loop of symptoms, leading to more severe hyperacusis and tinnitus, and corresponding changes to the effective function of the tensor tympani muscle.
A specific type of Tensor tympani syndrome called Tonic tensor tympani syndrome has been associated with hyperacusis patients. Tonic tensor tympani syndrome is an involuntary, anxiety based-condition where the acoustic reflex threshold for the tensor tympani muscle activity is reduced, resulting in more frequent spasm. This reflex can trigger symptoms from ear drum movements, Eustachian tube ventilations and trigeminal nerve irritability. Tonic tensor tympani syndrome has also been closely tied to a condition frequently experienced by those with hyperacusis called Acoustic Shock Disorder. Acoustic shock disorder can develop after exposure to an unexpected loud sound which is perceived as highly threatening, hyperacusis is the leading symptom experienced by those who experience Acoustic Shock Disorder. This study helped to identify that there is indeed a relationship between tensor tympani syndrome and hyperacusis.
Two other conditions that appear to frequently coexist with TTS symptoms are temporomandibular disorder (TMD) and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction. TTS symptoms, such as tinnitus or pain, in patients with TMD and TMJ dysfunction are most likely secondary to these temporomandibular disorders, TMJ dysfunction can also lead to symptoms of tinnitus and other hearing issues.
Another potential cause includes Eustachian Tube Dysfunction, which is common amongst those with a history of chronic ear infections, sinus infections or even severe seasonal allergies. The disruption to the function of the middle ear system can cause Tensor Tympani Syndrome in this patient population. This is due to the changes in middle ear pressure caused by the eustachian tube not opening and closing properly. This dysfunction within the eustachian tube leads to increased pressure on the eardrum and middle ear muscles which can cause these muscles to spasm in order to alleviate the increased pressure within the middle ear and provide relief to these delicate middle ear structures.
Finally, TTS symptoms have also been reported in some patients with trigeminal nerve irritability or trigeminal nerve neuralgia. Links have already been discovered between this condition and tinnitus, suggesting that conditions affecting nerves found in the auditory system and face may increase the possibility of co-morbid conditions within the same area.
Treatment Options For Tensor Tympani Syndrome
If you think you may be experiencing TTS, it’s important to talk to your doctor first. Auditory discomfort can have numerous root causes, and may be symptomatic of anything from stress to infection to perforation of the eardrum. It’s always best to rule out potential medical problems before seeking a singular course of treatment. You can visit an Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) doctor in your area to rule out objectively measurable dysfunction of the ears before moving on to rare or more difficult to diagnose conditions that lead to ear pain or damage to the inner ear. Once medically cleared, it is important to seek out professional treatments from licensed hearing professionals like those at Treble Health. Treatments that alleviate tinnitus and/or hyperacusis symptoms such as Tinnitus Retraining Therapy, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Sound Therapy have been shown to effectively reduce the severity of TTS symptoms in patients who experience these conditions as well as TTS. If you are searching for treatment options for TTS, we encourage you to schedule a complimentary telehealth consultation with our team. During this 20-minute Zoom call, we can answer any questions that you may have regarding TTS, and go over the different treatment options that are available for your specific situation.
Relaxation Techniques



Whether rooted in a medical condition or just a run-of-the-mill case of TTS, we strongly urge you to incorporate relaxation strategies into your care plan. Calming techniques can include a wide variety of strategies like meditation, yoga, or cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). These methods of increasing health are frequently included in comprehensive treatment plans of conditions like tinnitus and TTS, so getting a head start will not cause further damage to the function of the tensor tympani muscle, or lead to more ear pain.
While these exercises don’t eliminate TTS, they change the way our brains react to the pain of a flare-up or the fear that another TTS episode is just around the corner by helping us co-exist with the temporary discomfort. As a bonus: as you integrate stress relief measures into your daily life, you’re likely to both reduce the occurrences of tensor tympani syndrome and reap other health benefits, including better sleep and improved mental health.
Sound and Tinnitus Retraining Therapies
Another course of treatment is sound therapy. One effective tinnitus treatment method that uses sound therapy that can be useful for TTS symptom desensitization is Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT). Tinnitus Retraining Therapy was developed primarily for the treatment of tinnitus and hyperacusis. However, because there is a relationship between TTS and tinnitus/hyperacusis, Tinnitus Retraining Therapy can be helpful for all three conditions to reduce ear pain and discomfort and improve anxiety levels.
Again, the intervention isn’t designed to eliminate TTS or other ear maladies, but can be effective in providing relief by normalizing sounds through controlled amplification or variation of noise. Sound therapy is administered by specially-trained audiologists and is a safe, evidence-based way to help you better control how you react to flare-ups.
Multi-Team Treatments
Lastly, while there are no treatments with strong evidence base to support their efficacy, some patients have seen relief with Botox injections to help reduce the frequency of tensor tympani spasms. However, we encourage you to partner with your care team (ENT and audiologist) as you explore ways to find relief. An ENT physician can help you understand and navigate the range of options, keep tabs on what you’ve tried and how it’s worked, make sure you’re aware of emergent therapies, and act as a coordinator of care as you navigate therapies with your audiologist to find the right course of treatment for you.
Moving Forward with TTS Symptoms
Involuntary activation of the middle ear muscle reflex can lead to significant changes to quality of life and mental health. This particular syndrome is often accompanied by other issues, such as tinnitus and can lead to other concerns, including the onset of a regular tension headache, decreased social engagement and other close relationships, and can even initiate physiological reactions that make everyday functioning more difficult. Whether accompanied by mild tinnitus, a disorder of the facial nerve, or unaccompanied by any additional disorders or dysfunction, tensor tympani syndrome can significantly impact an individual’s overall health. Seeking treatment for the syndrome itself and the many additional symptoms that may arise can soothe a host of mental and physical maladies, in order to improve quality of life, develop a healthy relationship with everyday sounds and may even reduce the perception of pain.
Navigating through the struggles of TTS can be challenging, but the Treble Health team is here to guide you. Our seasoned audiologists, with decades of experience from top audiology practices nationwide, are committed to crafting a treatment plan tailored to your unique needs. We encourage you to schedule a complimentary telehealth consultation, offering you a no-strings-attached, 20-minute Zoom call to get all your questions answered and explore the various treatment options suited to your individual situation. Click here to schedule your personalized consultation and take the first step towards better audiological health.
Next Step: Book Free Consultation
- 75% of patients reduced their tinnitus within three months after following our recommendations.
- "I feel like Treble Health literally gave me my life back." - Randy S. (verified customer)
- Join thousands of people who have reduced their tinnitus after scheduling a free consultation.